This is one of a series of articles being produced by Aberdeen Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament (CND). You can read further articles in both past and future editions of Aberdeen Voice. With thanks to Jonathan Russell.
The Soviet nuclear testing site in present Kazakhstan is just one of the many places in the world that remain dangerously radioactive to this day.
The release of radiation, which is unique to nuclear explosions, has many horrendous effects.
The types of radiation include:
- Gamma
- Neutron
- Ionizing
These are emitted not only at the time of detonation but also for long periods afterwards. At the time of the detonation people are killed primarily by blast and thermal effects, with radiation a major factor only in a few cases, for it is mostly residue from radio-active fallout from the weapon debris, fission products, and in the case of ground burst, radiated soil. The radiation effects on people depend on:
- The amount of radioactive energy deposited in the body
- The ability of the radiation to harm human tissue
- The organs affected.
Areas affected include:
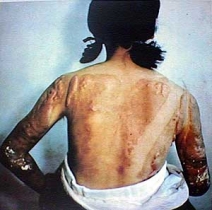
Hair- loss, leaving small clumps; the thyroid, which is particularly vulnerable to radiation; the blood system, affected for up to ten years with long term risk of leukaemia and lymphoma; it can cause heart failure; and at high levels brain damage leading to death; damage to the intestinal lining, leading to vomiting and diarrhoea – and eventually death; some victims will become sterile; long-term survivors are prone to cancer.
According to Japanese data, there was an increase in anaemia among people exposed to radiation. In some cases the decrease in white and red blood cells lasted up to ten years.
Cataracts were common in those partly shielded from the explosion.
Keloids, i.e. mounds of raised and twisted flesh, were found in 50-60 per cent of those burned by direct exposure to radiation.