Are you confused about which butter/margarine type spreads are healthy? Even if you aren’t then you probably should be! Craig Adams enlightens Voice readers.
Most people think they understand the difference between saturated, polyunsaturated, and monounsaturated fat, yet there are two key pieces of information relating to these that the food industry has deliberately occluded.
Firstly in terms of health, monounsaturated is best, then polyunsaturated, then saturated right?
Not quite – not all saturated fat is bad. Some saturated fats are among the healthiest fats of all. Furthermore, fat can turn into something chemically nasty when you heat it, and saturated fat is more resistant to this change than the other types of fat.
Unless you restrict frying to low temperatures, it’s actually safer to fry food in a saturated fat such as butter or lard. Unfortunately, telling people that would not help increase the sales of cooking oil.
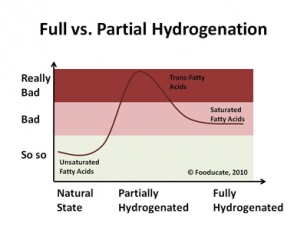
Secondly you may have observed that saturated fats are a solid grease, whereas unsaturated fats are oil? This is not mere coincidence, in fact it’s pretty much their defining trait. In order for an oil type unsaturated fat to become a spread, it somehow needs to be solidified. The reason that saturated fats are solid is because they are more saturated with hydrogen.
The process that makes a fat more solid is called hydrogenation, but it could just as easily be termed saturation… So in other words, to make an unsaturated fat more solid you saturate it, hence the issue with spreads.
Unfortunately because the public have been told that “saturated = bad” they’re probably going to look at the label, see how much saturated fat something contains, and judge it accordingly. Therefore the manufacturers tried to hydrogenate as little as possible, just enough to make it appear solid in the tub.
That’s why most of these spreads liquify almost on leaving the fridge; you’d be as well pouring oil on your toast! This is also where it turns nasty, because this “partial hydrogenation” has put the fat into an in-between state known as trans fatty acid, and trans fatty acid is very bad for you, much worse than saturated fat. Trans fatty acid kills.
Most products these days are labelled “Trans Fat Free!”… but that doesn’t mean they actually contain zero trans fatty acid. Oh no, no, no.
The politicians have allowed the manufacturers to label something “trans fat free” and even “zero trans fat”, provided it contains less than half a gram of trans fatty acid per serving.
That may not sound like much, but it’s 25% of the allegedly safe limit.
Since so many processed food now contain, ahem, “zero trans fat” there’s a high chance that you are unwittingly consuming way more than the 2g a day than may or may not be safe. Actually, let’s not beat around the bush, trans fatty acid is not safe.
Now here’s the ironic part. If you take an unsaturated fat, and you fully hydrogenate it, turning it into a saturated fat, there will be no trans fatty acid left in there. It will really contain zero trans fat, and actually be trans fat free. Although the now solid end result will be loaded with saturated fat, it’s not actually the bad kind of saturated fat, it’s just stearic acid, and your body will easily convert this back into a monounsaturated fat called oleic acid. No harm done whatsoever. It’s safe, and may even be healthy despite the saturated fat content.
Here is how to read the labels. Avoid anything that contains any: “trans fat”, “trans fatty acid”, “partially hydrogenated”, and plain old “hydrogenated” (because that is just marketing code for partially hydrogenated).
Anything containing “fully hydrogenated” is perfectly OK. The important part is “fully hydrogenated”. Now although a fully hydrogenated product will undoubtedly contain more saturated fat, this is a harmless type of saturated fat, so don’t be put off by it.
So just to clarify that last part: “fully hydrogenated” is safe whereas just plain old “hydrogenated” is a cunning marketing ploy, which really means “partially hydrogenated”, which is in turn just code for “trans fatty acid” – which kills.
100% fully hydrogenated products, although perfectly healthy, are extremely rare. This because the consumer is put off by the high saturated fat content.
Instead the manufacturer tends to thin out the hydrogenated fat with an unsaturated oil (yet more irony), in order to reduce the saturated fat content. This isn’t necessarily a bad thing, provided you refrain from heating the end result.
Also on the perfectly OK list is anything containing un-hydrogenated oil. In other words oil that has been left alone. There are some ‘oils’ such as coconut oil and palm oil, which are already high in saturated fat, and fairly solid at room temperature, that don’t require any hydrogenation.
This is why there are more and more products using palm oil. Palm oil is fine, although not as healthy as coconut oil, and in its refined (as opposed to virgin) state it’s not particularly good for you, but it’s way better than a trans fatty acid. The main problem with palm oil is that people are tearing down rain forests to plant palm trees.
So what about butter? Well butter is a naturally occurring almost entirely saturated fat. It does contain some naturally occurring trans fatty acid, but this is thought to be of a harmless nature (a hypothesis that has not yet been scientifically verified).
The saturated fat in butter is not all the good type, but it’s not all the bad type either, and at least butter is a natural unprocessed food. There are some spreadable butters now that have been blended with oils thereby reducing the overall saturated fat profile. Butter may not be a health food, but it certainly won’t kill you either. It’s certainly among the best of a bad bunch.
There is one saturated fat product that is believed to be healthy – coconut oil. This only contains the good saturated fat, is natural, and usually unprocessed (but check the label). Coconut oil is the safest fat you can use for any sort of frying. It may however impart a slight coconut taste to the food, and it’s quite expensive.
On the plus side it possesses both antibacterial and antiviral properties, promotes weight loss, and can help prevent Alzheimer’s disease. It’s all but a superfood. There even exists coco-butter, which can be used as a (slightly coconutty) substitute for butter and other spreads.
So to summarise:
- BAD = trans fat, trans fatty acid, partially hydrogenated, hydrogenated.
- OK = fully hydrogenated or un-hydrogenated.
- Butter is possibly healthier than most spreads, and safer for frying than cooking oil.
- Coconut oil is a healthy solid fat, and the safest thing to fry with. It’s actually very good for you, as are coconut milk and coconut cream.
As an aside, the most nutritious oils, or unsaturated fats, are hemp oil, closely followed by flaxseed oil, so use these for salad dressings. Both of these oils should be stored refrigerated at all times, and it’s doubtful that you’ll find any refrigerated oil in a supermarket, so best use a health food shop.
And lastly, there is absolutely nothing wrong with eating avocados. They are high in healthy fats, very good for you, and even aid weight loss.