With thanks to Esther Green, Senior Account Executive, Tricker PR.
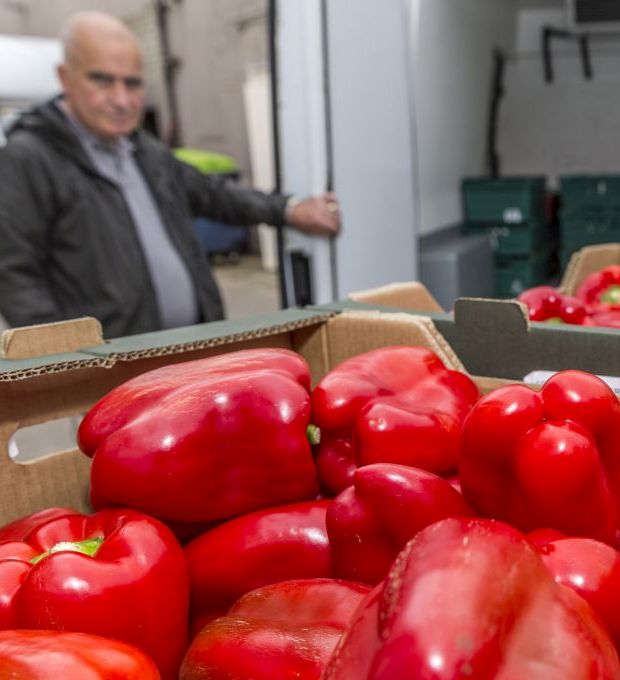 As food poverty continues to grow across Grampian – with the slump in the oil and gas industry pushing up requests for aid – a major financial firm is helping emergency food parcels reach those most in need.
As food poverty continues to grow across Grampian – with the slump in the oil and gas industry pushing up requests for aid – a major financial firm is helping emergency food parcels reach those most in need.
Aberdeen-based charity, Community Food Initiatives North East (CFINE) has a fleet of nine vehicles distributing food donations to organisations operating at grass roots levels to support those living in Aberdeen City, Aberdeenshire and Moray who are struggling to put a meal on the table.
Aberdeen Asset Management has donated £5,000 towards CFINE’s vehicle costs which has been described as a “fantastic contribution” that will help keep the fleet on the road, allowing it to continue to make essential deliveries to support the growing numbers of people affected by food poverty.
It’s not just those on benefits or low wages that gain assistance, the downturn in oil and gas resulted in a new market of referrals emerging, with laid-off energy sector workers forced to seek out vital support.
Dave Simmers, chief executive officer of CFINE said:
“To see your income collapse, sometimes with no warning at all, because of a job loss leads to difficult times. We have heard of people losing well paid jobs in the oil and gas sector but left with next to nothing when their income dries up – any one of us could be just be a few pay cheques away from a crisis.
“Our services are more needed than ever and with benefit changes coming through we expect there will be a deeper impact on already hard-pressed families. Many already have to make choices between heating or eating and we hear anecdotal evidence of parents going without food so they can buy their children’s school uniform.
“We operate on very tight budgets and every penny counts so to get £5,000 from Aberdeen Asset Management is a fantastic contribution. Without our vehicles, we could not get out to the charities and community organisations like Cyrenians, Salvation Army and Instant Neighbour which in turn reach the people in need in Grampian, which is a huge area to cover.”
CFINE is seeing increases for aid and the number of referrals increase all the time. In 2017 it will receive, organise and deliver more than 500 tonnes of food – which equates to a staggering 1,190,476 meals. Last year it distributed 10,000 emergency food parcels thorugh its own foodbank, a huge increase on the 3,000 food parcels given out in 2012, its first year of operation.
Dominic Kite of Aberdeen Asset Management’s charity committee said:
“Food poverty is a sad but very real fact of life for too many people in our region. We applaud the work of CFINE , its volunteers and partner organisations in tackling food poverty, building resilience and improving the health and wellbeing of people across the Grampian region.”
With demand for its services showing no sign of waning, CFINE has a number of volunteering opportunities and would welcome anyone who may be willing to help out. Call Christine or Graeme on 01224 596156; email info@cfine.org or visit the website www.cine.org to get involved. The charity also welcomes food and finanacial donations to ensure this vital work can continue.
The Aberdeen Asset Charitable Foundation was established in 2012 to formalise and develop the Group’s charitable giving globally and seeks partnerships with smaller charities around the world, where funds can be seen to have a meaningful and measurable impact.
The firm encourages its employees to use their time and skills to support its charitable projects. The main focus of the Foundation is around emerging markets and local communities, giving back to those areas which are a key strategic focus of the business and to build on the historic pattern of giving to communities in which Aberdeen employees live and work.
For more information visit http://www.aberdeen-asset.co.uk/aam.nsf/foundation/home
- Comments enabled – see comments box below. Note, all comments will be moderated.
 In a resounding victory for transparency, objectivity, and fair play, an Aberdeen City Senior Sustainable Development Officer was awarded 3 EcoCity Awards worth in the region of £1500 from Aberdeen City. The selection committee included academics, councillors, and several of the winner’s fellow ACC officers.
In a resounding victory for transparency, objectivity, and fair play, an Aberdeen City Senior Sustainable Development Officer was awarded 3 EcoCity Awards worth in the region of £1500 from Aberdeen City. The selection committee included academics, councillors, and several of the winner’s fellow ACC officers. By Suzanne Kelly.
By Suzanne Kelly.