Suzanne Kelly reports on the results of some important research presented at the recent Science Festival.
Aberdeen Science Festival had an amazing array of lectures, talks, trips and cabaret events which thousands of visitors enjoyed.
One of the more important issues covered was the very serious subject of second-hand smoke and its effect on children. I took the opportunity to talk to Dr Stephen Turner ( pictured ) of Aberdeen University and Rachel O’Donnell of ASH Scotland on a promising initiative to attempt to tackle this complex problem.
You smoke, or your partner smokes; you have a couple of children and a cat. No harm in smoking around them in the house – just open a window and the smoke can’t bother them. Can it?
You close the window when you’re done smoking. You don’t smell much smoke and you can’t see any clouds of smoke at all, so there’s no risk to anyone.
The truth is that ANY smoke residue can definitely harm your children and your pets. Smoke that you can see and other chemicals in smoke that you can’t see or smell are injuring kids. About 85% of cigarette smoke is invisible.
You might not believe this to be true, but please remember the old ‘canary in a coal mine’ story. Miners would take canaries down into the mines and if the bird suddenly died, either the oxygen was running out, or there was something dangerous, but invisible and scentless. Things you don’t see can indeed hurt you and your children.
REFRESH is an intervention aimed at reducing the exposure children get to second-hand smoke which was presented during the Aberdeen Science Festival. Dr Stephen Turner and Rachel O’Donnell were available to explain how they worked with smoking families when they did their research. They were not trying to make parents stop smoking, but instead were making people aware what the consequences can be on children’s lives. The full details are written in a paper called ‘REFRESH – reducing families’ exposure to second-hand smoke in the home: a feasibility study.’
Families where young children were living with regular smokers were asked to take part in a study which would measure indoor air quality in their homes. The personalised air quality data were presented to the smoker, then a motivational interview was held and positive solutions were suggested for cleaner, healthier air for the child.
There were about 60 Aberdonian participants in this study with each receiving four visits. At the first meeting a questionnaire was filled in to get a picture of the household members and their smoking habits; saliva samples were taken for chemical testing and monitoring equipment was set up. At the second visit the indoor air quality result was given to half of the households in addition to the motivational interview.
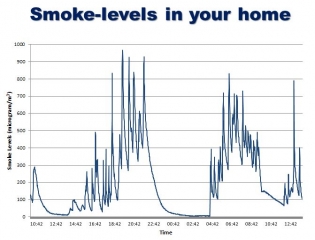
The chart below shows smoke levels in one study household.
Any quantity over 25 micrograms of smoke in a cubic metre of air space is harmful; the higher the figure, the more harm.
When the smoker was asleep, the levels dropped to non-existent. When the smoker lit that first cigarette, the levels went up to between 500 and 950 micrograms of smoke in a cubic metre of air.
Throughout the day, the smoke lingered – even when the smoker assumed the room was clear of smoke.
This came as quite a revelation for the smokers. Here is what some of them had to say:
“Seeing the results made a big difference. It was like a shock because I didn’t realise. Like I don’t sit here and smoke in front of my child, I do it in the kitchen, but for the readings to be high like that when I’m not like anywhere near it, if you know what I mean, it’s like a shock factor to realise what it can do. So I think that’s the best thing that like helped me.”
“I showed them how high it was, and some of them was like – you’re joking? And I was like no…”
“For it (monitoring) to be done in your own home and for you to know that the level of smoke is so high and you’re putting your children at risk of asthma, emphysema, all kinds of things, it’s quite shocking.”
One comment in particular shows the strength of the motivational factor provided by caring about children’s health:
“For me I think my son’s health, that’s my priority. So I would like to think that all mothers would think like that, that their kids come first no matter what. My bad habits shouldn’t be put onto my child. Because I can’t stop smoking doesn’t mean he has to suffer.”
After one month the research team revisited the houses, repeated the air quality measurements and, this time, gave all the households their results. During the month the air quality had not changed in the houses where air quality data was not initially given but air quality had improved by more than one third where the graph was used as part of the initial motivational interview.
personalised measurements of smoke in the home, while shocking, can also be very motivational
The trial was not large, but its results show that a future, large-scale programme would be beneficial. Like everything else, budgetary constraints are a factor. The vast sums that the NHS has to spend treating smoke-related illnesses should be sufficient to show that prevention should be actively pursued as one solution to the smoking issue.
The study has shown that lay people can most definitely engage with science and can understand complex matters when it is presented using clear, audience-appropriate, audience-relevant formats. Crucially, the personalised measurements of smoke in the home, while shocking, can also be very motivational. As the paper concludes:
“…in almost all participating households, indoor air (quality) approached a threshold considered unhealthy, suggesting a need to reduce indoor air (quality) in many households across the UK, and that many people would benefit from such an intervention.”
It seems that this combination of personalised data, positive suggestions and active participation of smokers might be the way to tackle smoke exposure to children. It is hoped this small study won’t be the end of the matter. The research goes on but, in the meantime, parents who smoke can create smoke free homes and smoke free cars to protect their children from the harmful effects of second hand smoke.
Smoking is still a social norm for many families but in the same way as drink driving and not wearing a seat belt are no longer acceptable, in future smoking will be considered as not acceptable by society.
PS for animal lovers – according to Dr Turner, the incidence of feline leukaemia is twice as high in cats that live in a smoker’s home than for cats that live in a smoke free environment.
- Comments enabled – see comments box below. Note, all comments will be moderated.